Images
Click any image to enlarge...
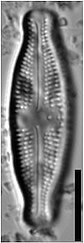
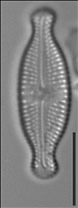
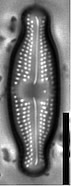
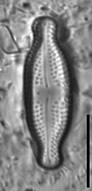
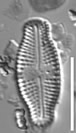
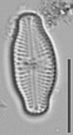
LM image scalebar = 10 µm = 72 pixels
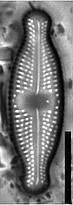
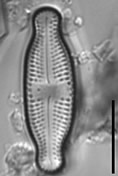
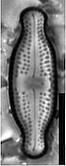
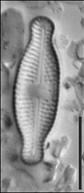
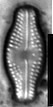
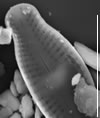
SEM image scalebar = 10 µm
Observations
| Observations: | Sarah Spaulding and Rhea Esposito |
|---|---|
| Length: | 12-17 µm |
| Width: | |
| Striae: |
Description:
Valves linear-lanceolate to elliptic-lanceolate in smaller valves, with distinctly convex margins and clearly protracted, capitate ends. In smaller valves, ends only rostrate to subrostrate. Valve length 11-31 µm, valve breadth 6.4-8.7 µm. Axial area narrow and linear, becoming larger towards the central area. Central area forming a rectangular to wedge-shaped stauros bordered on each side by one or - in larger specimens - rarely by 2 rows or areolae. One well-isolated, rounded stigma present. Raphe branches rather short and straight to weakly curved. Central raphe endings clearly deflected away from the stigma with slightly, expanded drop-like pores. Terminal raphe fissures short, weakly deflected and droplike expanded, terminating after the last transapical striae. Transapical striae radiate throughout, 15-17 in 10 µm, composed of 2-3 (very rarely 4) rounded to transapically elongated areolae. Outer row of areolae near the valve face margins clearly elongated. Areolae near the valve apices diverging forming a wedge-shaped hyaline area in the apices where the raphe fissures terminate. SEM: Externally, striae are not present at the valve/mantle interface. A single row of areolae is visible on the valve mantle. Distal raphe terminates in a narrow hyaline area. Stigma opens as a simple external pore. Internally, striae lack distinct openings and are transapically elongate. Stigma opening a curved and lipped slit.
| Morphology: | Naviculoid |
|---|---|
| Distribution: | South Victorialand endemic |
Autecology:
Notes:
Luticola austroatlantica can be separated from L. muticopsis (Van Heurck) Mann by its typical valve outline and the raphe structure. Luticola austroatlantica has distinctly convex margins presenting a rather symmetrical valve outline. Luticola muticopsis on the other hand, has one straight and one convex margin, presenting a clear asymmetrical outline. The valve apices in L. austroatlantica have a clear constricted base and a rounded outline. Although specimens of L. austroatlantica of Maritime Antarctic islands have a greater range (11-31 µm in length) than those of the Dry Valleys (12-17 µm in length), they form a distinct morphological range. The constriction is less pronounced in L. muticopsis. The central and terminal raphe endings in L. muticopsis are clearly hooked, not simply deflected whereas in L. austroatlantica they are simply deflected and droplike. Based on these differences, it is obvious that both species need to be separated formally. Furthermore, L. muticopsis is one of the most commonly reported taxa from the Antarctic (Kellogg and Kellogg 2002), and is widely misconstrued. The type of L. muticopsis is illustrated in Van de Vijver and Mataloni (2008). Another species that presents some similarities is Luticola murrayi (West et West) Mann non sensu Hustedt. The West & West (1911) type material demonstrates that Hustedt incorrectly extended the morphological variability of Luticola (Navicula) murrayi. It is possible that the Hustedt valves should be described as a separate species. Luticola murrayi sensu stricto has more areolae per stria and a more elongated valve outline with less pronounced apices as compared to L. austroatlantica. Luticola palearctica (Hustedt) Mann is larger in overall size with more expanded poles. Luticola truncata has more areolae per stria (4 vs. 3) and a more elliptical outline. The terminal raphe endings in the latter species are shorter and terminate before the last stria. In the central area, there are always two rows of areolae bordering one side of the stauros. Luticola austroatlantica also differs from Dry Valley taxa, L. muticopsis forma evoluta and L. muticopsis forma reducta West and West. Luticola muticopsis forma evoluta has a similar striae count (15-18 in 10 µm, as compared to 15-17 in 10 µm in L.
McMurdo Dry Valleys Waterbodies with Luticola austroatlantica
- Adams Stream
- Aiken Creek
- Blue Lake
- Bohner Stream
- Bowles Creek
- Canada Glacier
- Canada Stream
- Clear Lake
- Coast Lake
- Commonwealth Glacier
- Commonwealth Stream
- Crescent Stream
- Delta Stream
- Garwood Stream
- Green Creek
- Green Lake
- Harnish Creek
- Harnish Creek Tributary
- Huey Creek
- Hughes Glacier Pond
- Lawson Creek
- Little Sharpe
- Lost Seal Stream
- Lyons Tributary (Mason?)
- Many Glaciers Pond
- McKay Creek
- McMurdo Hut Ridge
- Miers Stream
- Onyx River
- Parera Pond
- Picture Pond
- Pond by Blue Lake
- Pond by Clear Lake
- Pond North of Rookery
- Pond South of Nussbaum Riegel
- Priscu Stream
- Spaulding Pond
- Upland Pond
- Von Guerard Stream
- Wales Stream
- Wharton Creek
- Wormherder Creek
Original Type Description
| Author: | Van de Vijver, Kopalová, Spaulding and Esposito 2008 |
|---|---|
| Length: | 11-31 µm |
| Width: | 6.4-8.7 µm |
| Striae: | 15-17 in 10 µm |
Original Description:
Valvae lineares-lanceolatae ad ellipticas-lanceolatas in speciminibus minoribus, marginibusque distincte convexis apicibusque protractis, capitatis sed rostratis in speciminibus minoribus. Valvae claro constrictae sub apicibus. Longitudo 11-31 µm, latitudo 6.4-8.7 µm. Area axialis angusta, linearis, dilatata ad aream centralem. Area centralis formans staurum cuneatam marginata a serie una (seriebus duabus in valvis maioribus) areolarum. Stigma solitaria elliptica adest. Raphe filiformis, recta vel leviter curvata terminationibus centralibus deflectis cum poris claro dilatatis. Fissurae terminales curtae, leviter deflexae et paene non expansae, semper terminantes post striam extremam. Striae transapicales moderate radiatae omnino, 15-17 in 10 µm, constantes ex 2-3 areolis potius magnis. Areolae ad apices divergentes formans aream cuneatam hyalinam. Areolae exteriores dilatatae.
New combination
| Author: |
|---|
Citations
Index Nominum Algarum (INA):
- If an INA link is available, it will be shown above
- The INA is a bibliographic reference "card file" for algal taxonomy, containing nearly 200,000 names of algae (in the broad sense).